Have you ever wondered, “what is ERP?” and how businesses can efficiently manage their complex operations while staying ahead in today’s fast-paced world? The answer lies in the power of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. These technological marvels are transforming the way companies handle their core business processes, streamlining workflows, and providing a single source of truth for data across departments. Buckle up, as we take you on a journey to explore the basics of ERP systems and how they can revolutionise your business operations.
Key Takeaways
ERP systems are powerful software platforms that integrate and automate core business processes to drive performance.
Implementing ERP systems can unlock benefits such as increased productivity, better decision-making, improved collaboration and cost savings.
With the right planning and strategy businesses can successfully overcome common challenges associated with ERPs while leveraging tailored solutions for industry specific needs.
Defining Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
ERP is like the central nervous system of a business, integrating and automating core business processes to provide a single source of truth for data and improving efficiency across departments. Imagine having a bird’s eye view of your entire organisation, with every department working in harmony, sharing information, and collaborating seamlessly. That’s the power of ERP systems.
At its core, an ERP system is a software platform designed to streamline business operations and enhance decision-making. From finance and supply chain management to manufacturing and human resources, enterprise resource planning software, also known as ERP systems, work diligently to bring everything together under one roof. They are like the masterminds of business intelligence, providing real-time data and insights to help drive business performance.
Whether you’re considering implementing a new ERP system or looking to upgrade your existing one, a successful ERP implementation can significantly improve supplier relationship management, data management, and overall business operations. However, gaining an understanding of the different components and their role in creating a unified and efficient system is significant.
So, how exactly does an ERP system function? We will delve into the fundamental elements of an ERP system and examine the key components that make it a formidable business instrument.
Components of an ERP System

An ERP system is like a well-oiled machine, with various modules working together to optimise specific business functions. Each module addresses a particular aspect of the business, providing employees with the transactions and insights they need to perform their jobs effectively. The modules that form the backbone of a comprehensive ERP solution include:
Finance
Supply chain management
Manufacturing
Customer relationship management
In the following sections, we’ll delve into three of the most critical modules of an ERP system – finance, supply chain management, and manufacturing – and discuss how they contribute to the overall efficiency and success of a business.
Finance
ERP for finance is like a superhero, swooping in to manage daily accounting and financial close processes with ease and accuracy. The finance module handles the following tasks:
General ledger management
Tracking of all financial data and transactions
Accounts payable and accounts receivable management
Timely reconciliations
Financial reporting
Compliance with reporting standards is vital for any business, and the finance module ensures this with ease. It ensures compliance with governing bodies like:
International Financial Reporting Standards Foundation (IFRS)
Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) for GAAP in the United States
Other international standards such as HGB in Germany and PCG in France
The finance module encompasses various sub-modules, including:
Financial accounting
Subledger accounting
Payables and receivables
Revenue management
Billing
Expense management
Project management
Asset management
Collections
With all these exciting modules at your disposal, managing your organisation’s finances can become a breeze with the right accounting software.
Supply Chain Management
Imagine having a crystal ball that could optimise your procurement, inventory, and logistics processes, enabling seamless collaboration and minimising costs. That’s what supply chain management modules in ERP systems can do for you.
The procurement module is like a well-trained procurement specialist, managing purchasing of raw materials or finished goods, automating requests for quotes and purchase orders, and optimising inventory levels when linked to demand planning. On the other hand, the inventory management module acts as a watchful guardian, displaying current inventory levels down to the SKU level, updating those numbers in real time, and accurately measuring key inventory-related metrics.
The order management module is the ultimate customer satisfaction champion, monitoring and prioritising customer orders from all channels, optimising progress through delivery, and significantly speeding up fulfillment and delivery times for a superior customer experience.
Lastly, the warehouse management module is like a seasoned warehouse supervisor, directing warehouse activities like:
receiving
picking
packing
shipping
It also identifies more efficient ways to execute these tasks, resulting in remarkable time and cost savings.
Manufacturing
The manufacturing module in an ERP system is like a master conductor, orchestrating every step of the production process, ensuring that production aligns with demand, and keeping track of in-progress and finished items. This powerful module has its roots in Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) software, which integrates core manufacturing components like:
purchasing
bills of materials
scheduling
contract management
MRP II brought about a revolution in manufacturing by:
Integrating different tasks into a common system
Offering an opportunity to leverage software to share and integrate enterprise data
Improving operational efficiency with enhanced production planning
Lowering inventory
Minimising waste
Today, modern ERP systems continue to build on the advantages of MRP II by seamlessly integrating:
Accounting and finance
Sales
Purchasing
Inventory
Manufacturing planning and scheduling
This offers manufacturers a unified system.
Advantages of Implementing ERP Systems
ERP implementation is like unlocking a treasure trove of benefits for your business. Some of the advantages of implementing ERP systems include:
Increased productivity
Better decision-making
Improved collaboration
Cost savings
The benefits of ERP systems are numerous and can greatly enhance your business operations.
By consolidating workflows and information in one place, ERP systems enable employees to easily view the progress of projects and the success of different business functions relevant to their jobs. Moreover, ERP systems can save organisations money by automating many simple, repetitive tasks, boosting overall productivity.
In the realm of decision-making, ERP software acts as a guiding light, offering total visibility and enabling management to access up-to-date data for informed decisions. Furthermore, ERP software enhances communication and collaboration, allowing workers to:
Check on the status of other departments
Inform their decisions
Lead to a synergised workforce
Boost productivity and employee satisfaction
Types of ERP Deployment Models
Similar to how a business requires the right foundation to expand and prosper, the selection of an appropriate ERP deployment model is indispensable for success. ERP systems can be deployed in three ways. These are on-premises, cloud-based, and hybrid deployments. Each of these options comes with its own set of advantages and considerations.
On-premises ERP systems give businesses control over their ERP software, security, maintenance, upgrades, and other fixes. However, this option often comes with higher upfront costs and requires dedicated in-house IT resources to manage the system.
Cloud-based ERP offers several advantages over traditional on-premise ERP systems, including:
Lower upfront costs
Greater scalability and agility
Easier integration
No need for hardware purchases or in-house IT experts
This option can be particularly advantageous for small and midsize businesses looking for cost-efficient ERP solutions.
Lastly, hybrid ERP deployment models combine the best of both worlds, with some ERP applications and data in the cloud and some on-premises. This option allows businesses to strike a balance between control and flexibility, tailoring their ERP deployment to best suit their unique needs and requirements.
Modern ERP Solutions and Trends
In the ever-evolving world of technology, modern ERP solutions are embracing intelligent technologies to help businesses run more efficient processes, leverage insightful data, and stay competitive. From AI and machine learning to robotic process automation (RPA) and the Internet of Things (IoT), modern ERP systems are incorporating cutting-edge technologies to provide enhanced automation, real-time insights, and scalability.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are transforming the way ERP systems analyse data, offering predictive insights and recommendations based on historical trends and patterns. This allows businesses to make more informed decisions and stay ahead of the curve in their respective industries.
Robotic process automation (RPA) is another exciting development in the ERP landscape. RPA is the automation of repetitive tasks. This enables employees to focus on value-added activities rather than spend all their time executing mundane tasks. RPA not only boosts productivity but also helps improve quality of work and employee job satisfaction.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is also playing a significant role in modern ERP systems, connecting devices and sensors to collect and analyse data in real-time. This allows businesses to monitor and optimise their operations more effectively, resulting in improved efficiency and cost savings.
Choosing the Right ERP Software
Choosing the appropriate ERP software might seem akin to locating a needle in a haystack. However, with a bit of guidance and a clear understanding of your business needs, you can identify the perfect fit for your organisation. Here are some factors to consider when choosing an ERP system:
First, evaluate your business requirements, including:
the organisation’s size
industry type
number of users
complexity of processes
desirable features
This will help you find an ERP solution that can best address your unique needs and requirements.
Second, consider the scalability options offered by the ERP software, such as the ability to add users, modules, and integrate with other systems. This will ensure that your ERP system can grow and adapt alongside your business.
Next, assess the user-friendliness of the ERP system, including its interface, customisation options, and accessibility from multiple devices. This will ensure that your employees can quickly adapt to the new system and start reaping its benefits.
Lastly, evaluate the vendor’s expertise, customer service, and reputation. A reliable and reputable vendor will provide you with the necessary support and resources to help you succeed with your ERP implementation.
ERP Implementation Lifecycle – Best Practices
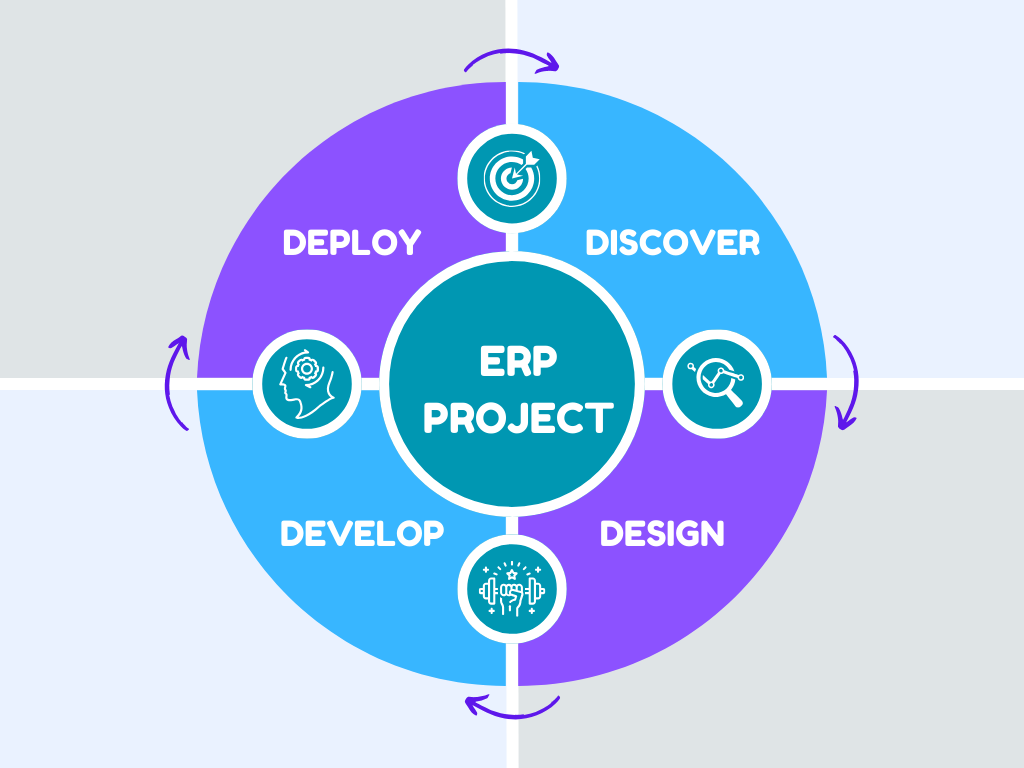
The process of implementing an ERP system can be intricate and demanding. However, with careful planning, clear communication, and adherence to best practices, you can set your business up for success. Here are some best practices to follow during your ERP implementation journey:
Begin with a thorough discovery and planning stage, where you determine your company’s needs from the ERP system, identify potential opportunities for growth, and pinpoint any inefficient processes that need to be addressed.
During the evaluation and selection stage, explore leading ERP offerings and choose a platform that can best resolve existing problems, meet the needs of all departments, and promote your company’s growth.
In the design stage, ensure that the ERP system can support your existing workflows and identify any processes that may need to change or require customisation. This will help you tailor the system to your business’s unique requirements.
Finally, during the development, testing, and deployment stages, configure the software to meet your defined needs, migrate your company’s data to the new solution, and plan how to train employees on the system. Prioritising employee training will ensure a smooth transition and help your team make the most of the new ERP system.
Modern cloud ERP software is constantly updated and improved, so it is important that an approach of continuous improvement is adopted by businesses. This allows them to take full advantage of the incremental improvements and new features that are regularly added to the system. Staying up to date with these enhancements can lead to more streamlined operations and increased efficiency.
Overcoming Common ERP Challenges
Despite the plethora of benefits offered by ERP systems, they can also pose certain challenges. Some common issues include system complexity, resistance to change, and integration obstacles. However, with proper planning and support, you can overcome these challenges and unlock the full potential of your ERP system.
To tackle system complexity, it’s important to devote time to comprehend the complexities of your ERP system and its integration with your current processes and workflows. By familiarising yourself with the system, you can identify areas where adjustments or customisations may be necessary for a seamless implementation.
Resistance to change is a natural part of any ERP implementation. To overcome this challenge, you can:
Involve key stakeholders and end-users throughout the planning and implementation process
Provide ample training and resources to help your team adapt to the new system
Communicate the benefits of the new system and address any concerns or fears
Foster a sense of ownership among your employees by involving them in decision-making and problem-solving
By following these steps, you can ensure a smoother transition and increase the likelihood of successful implementation.
Finally, integration issues can arise when implementing an ERP system, particularly when it comes to connecting with existing systems or third-party applications. To tackle this challenge, work closely with your ERP vendor or specialised consultants to develop a robust integration strategy that ensures seamless data flow and compatibility.
Industry-Specific ERP Applications

While different industries have unique needs and requirements in terms of business processes and software solutions, the beauty of ERP applications lies in their adaptability. They can be configured and tailored to cater to these distinct needs, allowing businesses in various sectors such as healthcare, retail, and manufacturing to automate and optimise their operations more effectively. This means that a general-purpose ERP system can be specifically configured for different industries like retail, ecommerce, or the construction industry. By tweaking the system’s functionalities and features, it can be adapted to meet the unique demands and challenges of each sector.
These tailored ERP applications are designed to fulfill the specific requirements of a particular industry, streamlining accounting, finance, and business management functions unique to that sector. As a result, industry-specific ERP configurations offer a great cost-benefit ratio without compromising on functionality.
Some examples of industries that can benefit from ERP software include automotive, wholesale distribution, and even niche sectors like fashion and foodservice. By implementing an industry-specific ERP system, these businesses can enhance their operations, reduce costs, and stay ahead of the competition.
In summary, industry-specific ERP applications provide businesses with a customised solution that addresses their unique needs and challenges, enabling them to thrive in their respective markets.
Case Studies: Successful ERP Implementations
Successful ERP implementations act as motivational examples for businesses intending to initiate their ERP journey. By examining real-world case studies, we can gain valuable insights into the benefits and lessons learned from these experiences.
Solara, a manufacturer of a comprehensive line of adjustable shading systems, patio covers, and canopies accelerated workflows and sped up project turnaround and delivery times. See Solara Case Study. After consolidating a plethora of disparate systems into a single, modern ERP solution, Solara experienced:
a 20% improvement in manufacturing productivity
improved production control
real-time access to business and customer data
Biscotti is a renowned patisserie delivering a range of baked goods and catering services. See Biscotti Case Study. Biscotti was struggling to meet demand due to inefficient operations and poor data visibility. After implementing a modern ERP, they saw immediate improvements:
increase in annual turnover of more than 20%
significant improvements in both the production and sales processes
improved product pricing analysis leading to better profitability
reduction in labour costs through the automation of daily orders
consolidation of scattered operations into a single logistics centre, leading to reduced picking and delivery times resulting in further cost saving
Each of these companies faced unique challenges during their ERP implementation, but with proper planning, communication, and adherence to best practices, they were able to overcome these obstacles and achieve stellar results.
Summary
In conclusion, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are formidable tools that can significantly transform the way businesses operate. By integrating and automating core business processes, they streamline workflows and provide a single source of truth for data across departments. This results in improved efficiency and a harmonious collaboration among various sectors of the organisation.
The various components of an ERP system, including finance, supply chain management, and manufacturing modules, work synergistically to optimise specific business functions. They equip employees with the necessary transactions and insights to perform their roles effectively, thereby driving overall business performance.
The deployment models of ERP systems, be it on-premises, cloud-based, or hybrid, offer businesses the flexibility to choose a model that best suits their unique needs and requirements. Each of these options comes with its own set of advantages and considerations, allowing businesses to strike a balance between control and flexibility.
Furthermore, modern ERP solutions are embracing cutting-edge technologies like AI, machine learning, RPA, and IoT. These intelligent technologies provide enhanced automation, real-time insights, and scalability, helping businesses to run more efficient processes, leverage insightful data, and stay competitive.
Industry-specific ERP applications cater to the distinct needs of various sectors, allowing businesses to automate and optimise their operations more effectively. By implementing an industry-specific ERP system, businesses can enhance their operations, reduce costs, and stay ahead of the competition.
The successful implementation of ERP systems, as evidenced by case studies, can bring about a host of benefits such as increased productivity, better decision-making, improved collaboration, and cost savings. However, it’s important to remember that proper planning, clear communication, and adherence to best practices are crucial for a successful ERP implementation.
In essence, by understanding the various components, deployment models, and industry-specific applications of ERP systems, as well as following best practices and learning from successful case studies, businesses can harness the full potential of ERP systems. This will enable them to streamline their operations, make informed decisions, and ultimately soar to new heights of success.